Antifungal Treatments
There are TWO main classes of antifungal agents for the treatment of fungal skin infections:
| Class of antifungal agent | Allylamine | Azole |
| Example of antifungal | Terbinafine | Clotrimazole |
| Mode of action | Fungicidal Fungal cell death | Fungistatic Fungal cell growth arrest |
Both classes of antifungal agents work by interfering with fungal cell wall synthesis,
HOWEVER
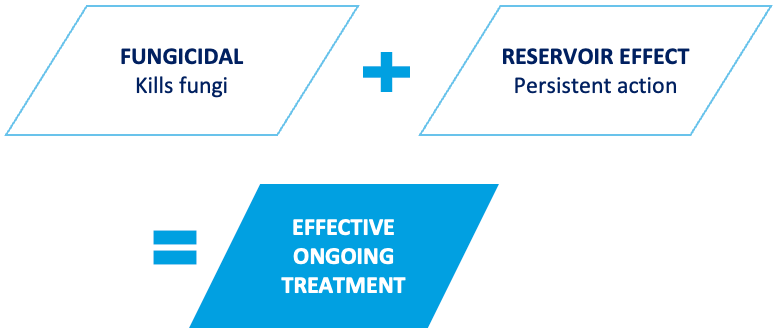
Fungicidal agents, such as terbinafine kills the fungal organism and has a shorter treatment time and often higher cure rates compared to fungistatic agents.
Benefits of Terbinafine
Allylamines (such as terbinafine)
- Short treatment course
- Low relapse rate
The fungicidal action of terbinafine allows it to bind to corneocytes (cells that make up the outermost layer of the epidermis) and remain in the outermost layer of the epidermis creating a ‘reservoir effect’, thus reducing the treatment course and provides lasting protection against the recurrence of symptoms.